Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMJ3I1Q)
| Drug Name |
Niflumic Acid
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Actol; Donalgin; Flunir; Forenol; Landruma; NFL; Niflactol; Niflam; Niflugel; Niflumate; Nifluril; Acide niflumique; Acide niflumique [French]; Acido niflumico; Acido niflumico [Italian]; Acidum niflumicum; Nifluminic acid; UPSA Conseil Brand of Niflumic Acid; Upsamedica Brand of Niflumic Acid; N 0630; SC 1332; UP 83; UPSA Brand 1 of Niflumic Acid; UPSA Brand 2 of Niflumic Acid; Acid, Niflumic; Acide niflumique [INN-French]; Acido niflumico [INN-Spanish]; Acidum niflumicum [INN-Latin]; Niflugel (TN); Niflumic acid (INN); Niflumic acid [INN:DCF]; Aza-2 dimethyl-2',3' (tetrazolyl-5)-6 diphenylamino; Aza-2 dimethyl-2',3' (tetrazolyl-5)-6 diphenylamino [French]; 2-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)-phenyl)aminonicotinic acid; 2-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)anilino)nicotinic acid; 2-(3-Trifluoromethyl-phenylamino)-nicotinic acid; 2-(3-Trifluoromethylanilino)nicotinic Acid; 2-(3-[Trifluoromethyl]anilino)nicotinic acid; 2-(A,A,A-Trifluoro-m-toluidino)nicotinic acid; 2-(alpha,alpha,alpha-Trifluoro-m-toluidino)nicotinic acid; 2-[(3-TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PHENYL]AMINO-3-PYRIDINE-CARBOXYLIC ACID; 2-[(3-Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]-3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid; 2-[(3-Trifluoromethylphenyl)amino]nicotinic Acid; 2-[3-(Trifluoromethyl)anilino]nicotinic acid; 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]pyridine-3-carboxylic acid; 2-[alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-m-toluidino]-nicotinic acid; 2-{[3-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PHENYL]AMINO}NICOTINIC ACID; 2-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}pyridine-3-carboxylic acid; 39690A
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
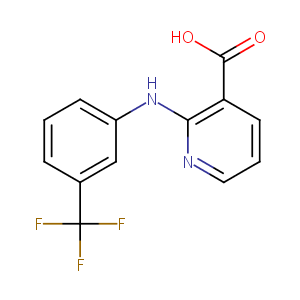 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 282.22 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | FA20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
